Which Statement Explains One Reason Why Unconformities Occur?
Introduction to Unconformities
Unconformities are one of geology’s most fascinating features. They represent missing pieces in Earth’s geological puzzle, revealing much about the planet’s history, even when they show periods where time essentially “went missing.” But why do these gaps, or unconformities, occur in the first place? Let’s dive deep to understand the Reason Why Unconformities Occur and the role they play in shaping our understanding of Earth’s geological record.
What are Unconformities?
Unconformities can be a bit tricky to wrap your head around at first, but they are incredibly important in geology. Essentially, an unconformity represents a break in the geological record. It’s like opening a history book and discovering several pages have been ripped out.
Basic Definition of Unconformities
At its core, an unconformity is a gap in time within the rock layers. It means that layers of rock that should have formed during a particular period are either missing or didn’t form at all.
Types of Unconformities
There are three main types of unconformities, and each one tells its own unique story about Earth’s geological history.
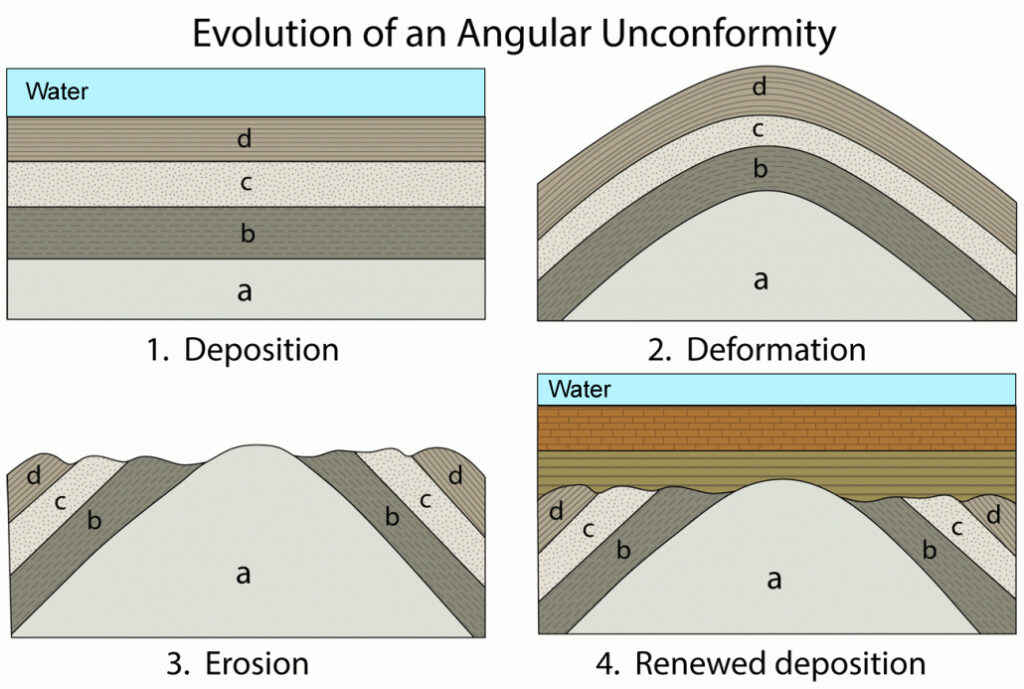
Angular Unconformity
This type of unconformity occurs when older layers of rock are tilted or folded and then eroded. Younger, more horizontal layers of sediment then form on top, creating a visible gap in the geological timeline.
Disconformity
A disconformity is when layers of sediment are parallel but there’s still a noticeable time gap between them. In this case, erosion might have wiped out some layers, or sediment simply wasn’t deposited for a period.
Nonconformity
This occurs when sedimentary rock lies on top of older, eroded igneous or metamorphic rock. The time gap between the two is often vast, and the contrast between the rock types is striking.
How Unconformities Form
Understanding how unconformities form is essential to grasp why they occur. The processes involved are quite complex, involving the interplay of erosion, tectonic activity, and shifts in sea levels.
Erosion and Sedimentation: The Main Culprits
Erosion is one of the biggest factors in the formation of unconformities. Over time, wind, water, and ice can wear away at layers of rock, creating significant gaps in the geological record. Once erosion has stripped away these layers, new sediment may be deposited on top, leaving a gap in the timeline.
Role of Geological Forces
Geological forces, like tectonic movements, play a big part in forming unconformities. As plates shift, rocks can be pushed up (uplift) or down (subsidence), leading to periods where sedimentation slows down or stops entirely. This gap in deposition results in unconformities.
Why Unconformities Occur
Now, let’s get to the heart of the matter. Why do unconformities occur in the first place? What’s happening on our planet that leads to these gaps in the geological record?
Tectonic Activity and Plate Movements
Earth’s tectonic plates are in constant motion, and this movement is one of the primary causes of unconformities. When plates shift, they can cause rocks to be uplifted or submerged.
Uplift and Subsidence
When an area of the Earth’s crust is uplifted, erosion can speed up, stripping away layers of rock faster than new layers can form. Subsidence, on the other hand, can cause areas to sink below sea level, slowing sediment deposition, which may eventually result in a gap or unconformity.
Changes in Sea Levels
Sea level fluctuations also play a role in unconformities. When sea levels drop, land that was previously underwater may be exposed to erosion. When the sea level rises again, new layers of sediment cover the eroded surface, leaving behind an unconformity.
Erosion: A Major Contributor
Erosion doesn’t always occur at a constant rate. Periods of intense erosion, followed by calm periods where little or no sediment is deposited, lead to time gaps in the rock record. These gaps are prime locations where unconformities form.
The Importance of Unconformities in Geology
Unconformities might seem like gaps or missing pieces in the geological story, but they actually tell us a lot about Earth’s history. They help geologists understand changes that happened on our planet millions of years ago.
Identifying Unconformities
Unconformities aren’t always easy to spot, but geologists have several tools and techniques to help them identify these important geological features.
Tools and Techniques
Geologists use everything from satellite imagery to deep core samples to identify unconformities. These methods help them see the gaps in sedimentary layers and analyze the surrounding rock for clues.
Field Observations and Laboratory Analysis
In the field, geologists rely on visual cues—like changes in rock types and angles between layers—to spot unconformities. In the lab, they use advanced dating techniques and microscopic analysis to determine the age of the rocks and the time gaps between layers.
Conclusion: The Significance of Unconformities
In conclusion, unconformities might seem like gaps in the Earth’s story, but they are actually filled with valuable information. They help us understand past climates, tectonic movements, and even life on Earth. Without these gaps, the story of our planet would be much harder to piece together.



